Where does electroslag pressure welding flux sel
Steel bar electroslag pressure welding is a pressure welding method that places two steel bars into a vertical butt joint form, uses the welding current to pass through the gap between the two steel bars, forms an arc process and electroslag process under the flux layer, generates arc heat and resistance heat, melts the steel bar and pressurizes.

The welding process of electroslag pressure welding includes four stages: arc striking process, arc process, electroslag process and jacking process.
At the beginning of welding, first ignite the arc between the upper and lower reinforcement end faces to melt the flux around the arc and form holes; Then, the welding arc burns between the two reinforcing bars, the arc heat melts the ends of the two reinforcing bars, the molten metal forms a molten pool, and the molten flux forms slag (slag pool) to cover the molten pool. At this time, with the combustion of the arc, the carbonyl parts of the upper and lower reinforcing bars gradually melt, and the upper reinforcing bars are continuously sent down to maintain the stability of the arc and continue the arc process; With the continuation of the arc process, the melting amount at the ends of the two reinforcing bars increases, and the molten pool and slag pool deepen. When reaching a certain depth, speed up the feeding speed of the upper reinforcing bar to make its end directly contact with the slag pool. At this time, the arc extinguishes and the arc process becomes electroslag process; When the resistance heat generated in the electroslag process makes the ends of the upper and lower reinforcement reach the uniform heating of the whole section, quickly press the upper reinforcement down, squeeze out all slag and liquid metal, and then cut off the welding power supply to complete the welding work.
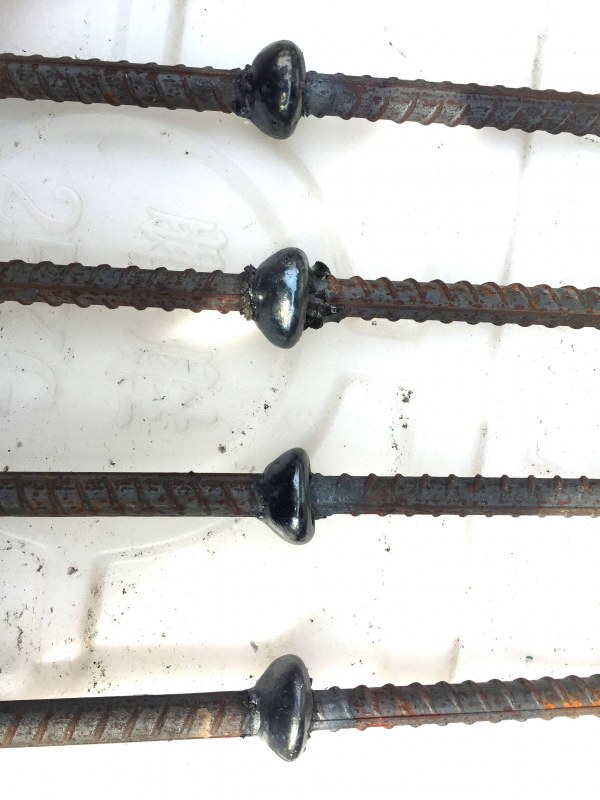

Electroslag pressure welding is suitable for the connection of vertical or inclined (inclination within 4:1) reinforcement in cast-in-situ reinforced concrete structures, especially for column and wall reinforcement of high-rise buildings.